Diapers are indispensable in modern childcare and adult incontinence management, where comfort and functionality are critical. Among the key materials used in diaper construction, non-woven side tapes play a vital role, not only for secure fastening but also for enhancing the overall breathability of the diaper. This article delves into the mechanisms by which non-woven side tapes influence diaper breathability, emphasizing their composition, structure, and functional attributes.
1. Overview of Diaper Breathability
Breathability in diapers refers to their ability to allow the passage of air and water vapor while preventing the leakage of liquids. It is crucial for maintaining skin health by reducing moisture accumulation and preventing conditions such as diaper rash. The breathability of a diaper is influenced by several components, including the top sheet, absorbent core, backsheet, and fastening systems like side tapes. Each component must work cohesively to strike a balance between containment and ventilation.
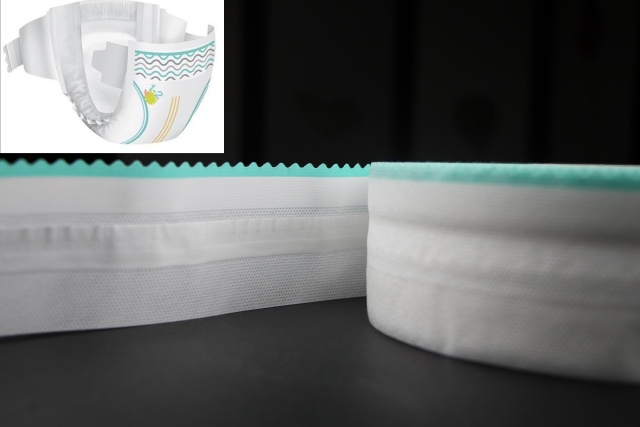

2. The Role of Non-Woven Side Tapes in Diapers
Non-woven side tapes are the fastening components that ensure a snug and adjustable fit. Typically made from polypropylene (PP) or polyethylene (PE), these tapes consist of multiple layers, often including a non-woven base layer, an adhesive layer, and a hook or loop material for attachment. While their primary function is mechanical fastening, they also contribute significantly to the diaper's overall performance, including its breathability.
2.1 Material Composition
Non-woven fabrics are created by bonding fibers through mechanical, thermal, or chemical methods. The porosity and permeability of the non-woven layer play a pivotal role in air and vapor exchange. Materials like spunbond or meltblown PP are commonly used due to their lightweight, breathable, and durable characteristics. When integrated into diapers, these materials enhance air circulation around the fastening zones.
2.2 Structural Design
The microstructure of non-woven side tapes, characterized by interconnected pores, facilitates the movement of air and water vapor. This structural feature helps in dissipating heat and moisture generated within the diaper, especially in areas prone to compression, such as around the waist and thighs. Furthermore, advanced manufacturing techniques allow for precise control over pore size and distribution, optimizing breathability without compromising strength.
3. Mechanisms of Breathability Enhancement
Non-woven side tapes enhance diaper breathability through several mechanisms:
3.1 Vapor Permeability
The intrinsic porosity of non-woven materials enables water vapor to escape from the diaper interior. This property is especially important for reducing humidity and maintaining a dry microclimate near the skin. Studies have shown that diapers with breathable side tapes significantly lower skin hydration levels compared to those with non-breathable alternatives.
3.2 Heat Dissipation
By allowing air exchange, non-woven side tapes facilitate heat dissipation from the diaper's surface. This cooling effect is crucial for wearer comfort, particularly in warm climates or during prolonged use.
3.3 Moisture Transport
In addition to allowing vapor transmission, the hydrophobic nature of non-woven fabrics prevents liquid water from seeping through. This dual functionality ensures that the diaper remains dry externally while maintaining internal breathability.
4. Challenges and Considerations
Despite their benefits, the integration of non-woven side tapes into diapers poses certain challenges:
4.1 Balance Between Strength and Breathability
Ensuring that non-woven side tapes are strong enough to withstand repeated fastening while remaining breathable is a key technical challenge. Manufacturers must optimize the fiber composition, bonding methods, and structural design to achieve this balance.
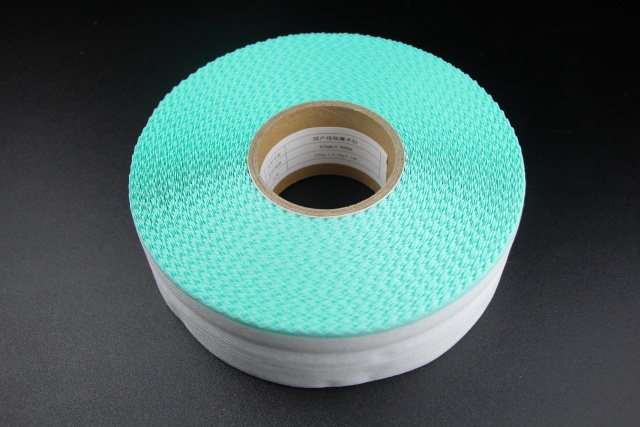

4.2 Compatibility with Other Components
The breathability of side tapes must align with that of the backsheet and other diaper layers to prevent localized heat and moisture buildup. Poor integration can lead to uneven ventilation, reducing the overall efficacy of the diaper.
4.3 Environmental Impact
As sustainability becomes a priority, the use of non-woven materials raises concerns about their environmental footprint. Developing biodegradable or recyclable non-woven side tapes is an ongoing area of research.
5. Innovations and Future Trends
Advances in material science and manufacturing techniques continue to drive innovation in non-woven side tapes:
5.1 Smart Materials
The development of smart non-woven fabrics with adaptive breathability, responding to temperature or humidity changes, represents a promising avenue. These materials can enhance wearer comfort dynamically, improving the user experience.
5.2 Sustainable Alternatives
Eco-friendly non-woven fabrics made from biodegradable polymers or recycled fibers are gaining traction. These materials reduce the environmental impact of disposable diapers without compromising functionality.
5.3 Enhanced Manufacturing Techniques
Technologies such as electrospinning and nanofiber integration enable the production of ultra-thin, highly breathable non-woven layers. These advancements provide new possibilities for optimizing the performance of side tapes.
6. Conclusion
Non-woven side tapes are indispensable components that significantly influence the breathability of diapers. Through their material composition, structural design, and functional mechanisms, they contribute to creating a more comfortable and skin-friendly product. However, achieving optimal performance requires careful consideration of trade-offs between breathability, strength, and sustainability. As technology progresses, innovations in non-woven materials and manufacturing processes will continue to enhance the functionality and environmental compatibility of diapers, meeting the evolving needs of users and the market.


